COPD Early Signs & Treatments
Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease (COPD) is a progressive condition that restricts airflow and makes breathing difficult. Early symptoms—like persistent coughing, wheezing, or shortness of breath—are often overlooked, delaying proper diagnosis and care
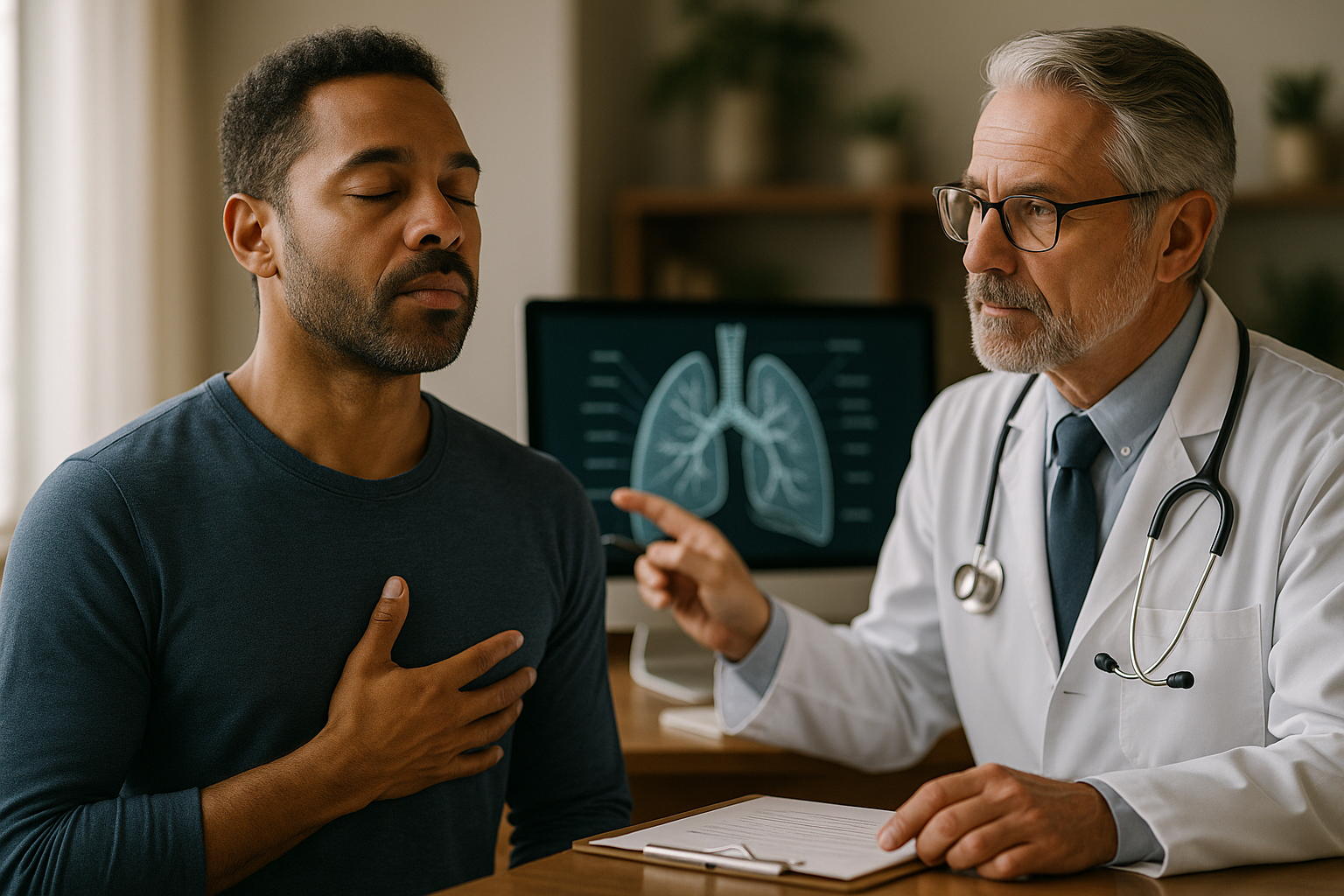
What are the earliest signs of COPD?
The early signs of COPD can be subtle and easily mistaken for other conditions. Common early symptoms include:
-
Persistent cough, often called a “smoker’s cough”
-
Increased mucus production
-
Shortness of breath, especially during physical activities
-
Wheezing or whistling sound when breathing
-
Frequent respiratory infections
These symptoms may develop gradually, making it challenging for individuals to recognize them as signs of a more serious condition. It’s important to pay attention to any changes in breathing patterns or lung function, especially if you have risk factors for COPD, such as a history of smoking or exposure to air pollutants.
How is COPD diagnosed in its early stages?
Early diagnosis of COPD is crucial for effective management and slowing disease progression. Diagnosis typically involves:
-
Medical history review: Your doctor will ask about symptoms, smoking history, and exposure to environmental pollutants.
-
Physical examination: This includes listening to your lungs and checking for signs of respiratory distress.
-
Spirometry test: This simple breathing test measures how much air you can exhale and how quickly.
-
Chest X-ray or CT scan: These imaging tests can help rule out other conditions and assess lung damage.
-
Blood tests: These may be used to check oxygen levels and rule out other conditions.
Early-stage COPD can be challenging to diagnose, as symptoms may be mild. Regular check-ups and open communication with healthcare providers are essential, especially for those at higher risk.
What are the different stages of COPD?
COPD is typically classified into four stages based on the severity of airflow limitation:
-
Stage 1 (Mild): Mild airflow limitation with minimal symptoms
-
Stage 2 (Moderate): Worsening airflow limitation with noticeable symptoms
-
Stage 3 (Severe): Significant airflow limitation with frequent exacerbations
-
Stage 4 (Very Severe): Severe airflow limitation, potentially life-threatening
Each stage is determined by lung function tests and symptom severity. As COPD progresses, symptoms become more pronounced, and daily activities may become increasingly difficult. Early detection and treatment can help slow the progression through these stages.
What treatments are available for early-stage COPD?
Early-stage COPD treatment focuses on symptom management and slowing disease progression. Common treatments include:
-
Smoking cessation: This is the most important step in managing COPD at any stage.
-
Bronchodilators: These medications help relax and open airways, making breathing easier.
-
Inhaled corticosteroids: These may be prescribed to reduce airway inflammation.
-
Pulmonary rehabilitation: This program combines exercise, education, and support to improve lung function and quality of life.
-
Lifestyle changes: Regular exercise, a healthy diet, and avoiding air pollutants can help manage symptoms.
Early treatment can significantly improve outcomes and quality of life for individuals with COPD. It’s essential to work closely with healthcare providers to develop a personalized treatment plan.
How can COPD be prevented or its progression slowed?
While COPD cannot always be prevented, several steps can reduce risk and slow progression:
-
Avoid smoking and secondhand smoke exposure
-
Protect yourself from occupational dust and chemical fumes
-
Get vaccinated against respiratory infections like flu and pneumonia
-
Exercise regularly to maintain lung function
-
Maintain a healthy diet rich in antioxidants
In Worldwide, air pollution is a significant concern for respiratory health. Staying informed about local air quality and taking precautions on high-pollution days can help protect your lungs.
What are the latest advancements in COPD treatment?
Recent advancements in COPD treatment offer new hope for patients:
-
Combination inhalers: These combine multiple medications in a single device for easier use.
-
Biologics: New targeted therapies can help reduce inflammation in some COPD patients.
-
Endobronchial valves: These devices can help improve lung function in select patients with severe emphysema.
-
Digital health tools: Apps and wearable devices can help monitor symptoms and improve treatment adherence.
-
Stem cell therapy: While still experimental, this shows promise for repairing lung damage.
| Treatment | Provider | Key Features |
|---|---|---|
| Combination Inhalers | Various pharmaceutical companies | Ease of use, multiple medications in one device |
| Biologics | Specialized clinics | Targeted therapy for specific COPD phenotypes |
| Endobronchial Valves | Pulmonary specialists | Minimally invasive option for severe emphysema |
| Digital Health Tools | Various tech companies | Remote monitoring, improved adherence |
| Stem Cell Therapy | Research institutions | Experimental treatment for lung repair |
COPD is a complex condition that requires ongoing management and care. By recognizing early signs, seeking prompt diagnosis, and adhering to treatment plans, individuals with COPD can significantly improve their quality of life and slow disease progression. Regular follow-ups with healthcare providers and staying informed about new treatments are essential components of effective COPD management.
This article is for informational purposes only and should not be considered medical advice. Please consult a qualified healthcare professional for personalized guidance and treatment.




